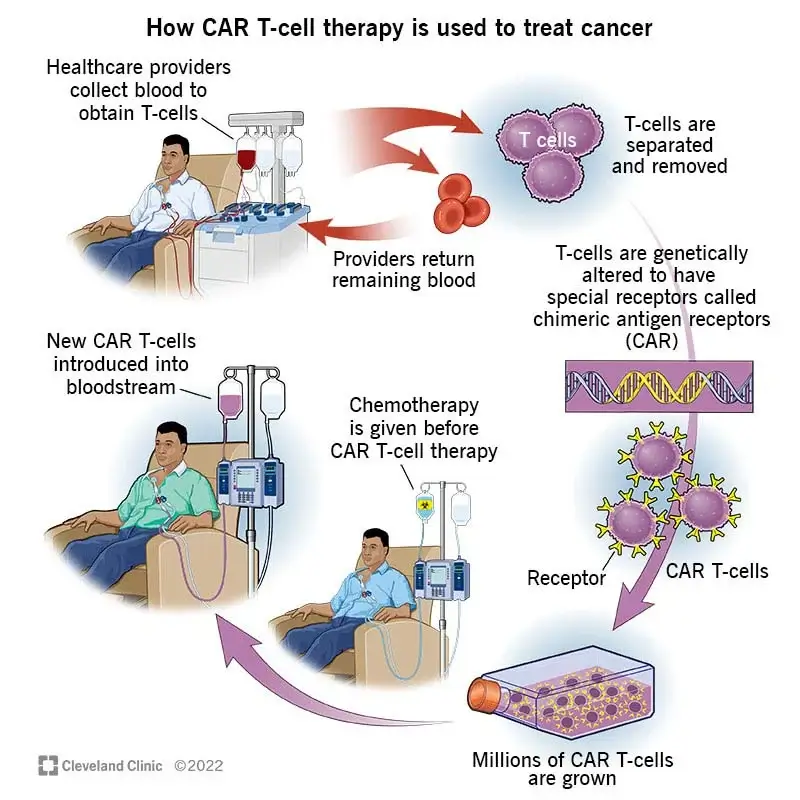
How CAR T-cell therapy works
Immune receptors and foreign antigens
The immune system recognizes foreign substances in the body by finding proteins called antigens on the surface of those cells. Immune cells called T cells have their own proteins called receptors that attach to foreign antigens and help trigger other parts of the immune system to destroy the foreign substance.
The relationship between antigens and immune receptors is like a lock and key. Just as a lock can only be opened with the right key, each foreign antigen has a unique immune receptor that is able to bind to it.
Cancer cells also have antigens, but if your immune cells don’t have the right receptors, they can’t attach to the antigens and help destroy the cancer cells.
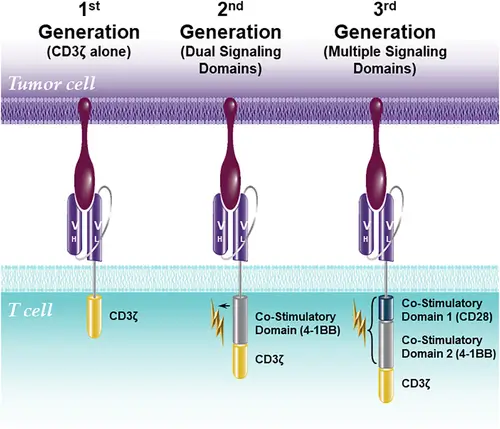
Chimeric antigen receptors (CARs)
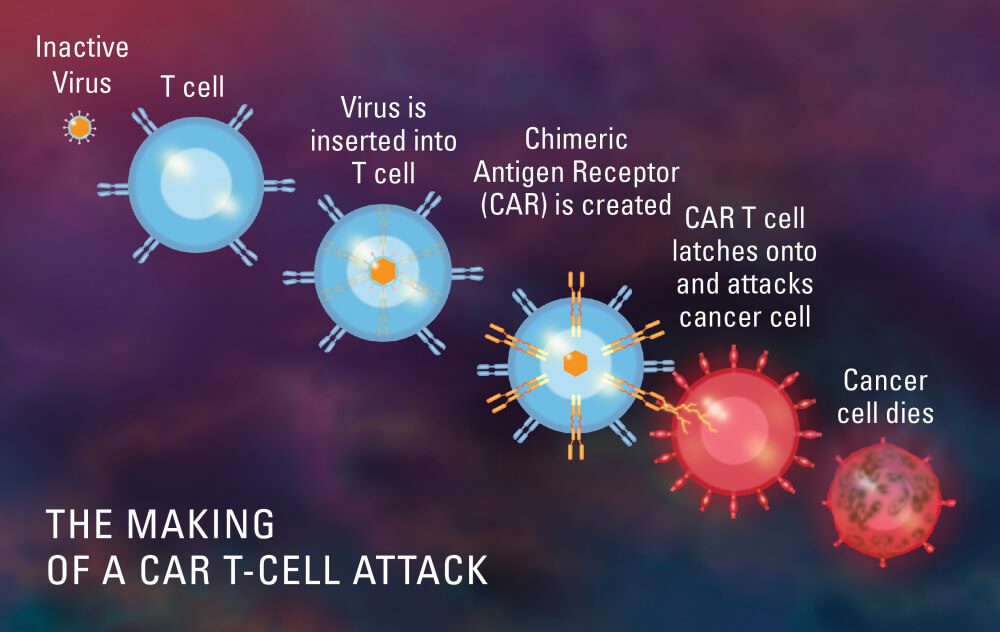
In CAR T-cell therapies, T cells are taken from the patient’s blood and are changed in the lab by adding a gene for a receptor (called a chimeric antigen receptor or CAR), which helps the T cells attach to a specific cancer cell antigen. The CAR T cells are then given back to the patient.
Since different cancers have different antigens, each CAR is made for a specific cancer’s antigen. For example, in certain kinds of leukemia or lymphoma, the cancer cells have an antigen called CD19. The CAR T-cell therapies to treat these cancers are made to attach to the CD19 antigen and will not work for a cancer that does not have the CD19 antigen.
CAR-T Cell therapy in China
A type of treatment in which a patient’s T cells (a type of immune system cell) are changed in the laboratory so they will attack cancer cells. T cells are taken from a patient’s blood. Then the gene for a special receptor that binds to a certain protein on the patient’s cancer cells is added to the T cells in the laboratory. The special receptor is called a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR). Large numbers of the CAR T cells are grown in the laboratory and given to the patient by infusion. CAR T-cell therapy is used to treat certain blood cancers, and it is being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer. Also called chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy.
CAR-T Therapy Approved At Home And Abroad
| Name of the drug | Enterprise | Indications | Target | Selling price | Time to approval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
KYMRIAH | t is used to treat patients (≤ 25 years of age) with relapsed (relapse after remission with treatment) or refractory acute B-line lymphoblastic leukemia (B-line r/r ALL). Complete response rate (CR) greater than 90% | CD19 | $47.5 | United States, 2017/8/30 |
 |
YESCARTA | CYESCARTA is a therapy for adults with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma, including large B-cell lymphoma. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma complete response rate (CR): 51% | CD19 | $37.3 | 2017/10/18 |
 |
YESCARTA | For the treatment of relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma, the overall response rate is 93%, and the complete response rate is 67% | CD19 | $37.3 | 2021/10/1 |
 |
Breyanzi | For the treatment of large B-cell lymphoma, the overall response rate is 73%, and the complete response rate is 54% | CD19 | $41.03 | 2017/10/18 |
 |
Breyanzi | For the treatment of multiple myeloma, the overall response rate is 72%, and the complete response rate is 28% | CD19 | $41,95 | 2021/3 |
 |
Relma-cel | For the treatment of large B-cell lymphoma, the overall response rate is 75.9%, and the complete response rate is 51.7% | CD19 | 129million RMB | China 2021/09 |
 |
Carvykti | For the treatment of large B-cell lymphoma, the overall response rate is 73%, and the complete response rate is 54% | CD19 | 293million RMB | China 2022/02 |
CAR-T therapy has made significant advancements in treating lymphoma in China. Chinese researchers and medical institutions have conducted extensive clinical trials, yielding promising results. CAR-T therapy involves modifying a patient’s T cells to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), enabling the cells to recognize and target cancerous cells.
Since 2017, research on CAR-T therapy in China has progressed rapidly. In the field of lymphoma, CAR-T therapy has shown remarkable efficacy against refractory and relapsed B-cell lymphomas. Clinical trials have demonstrated high response rates, with a significant number of patients achieving complete remission.
Several CAR-T therapies have gained approval from regulatory authorities in China. Notable examples include Kymriah (tisagenlecleucel) and Yescarta (axicabtagene ciloleucel), which have been registered as drugs and expanded their indications for the treatment of lymphoma.
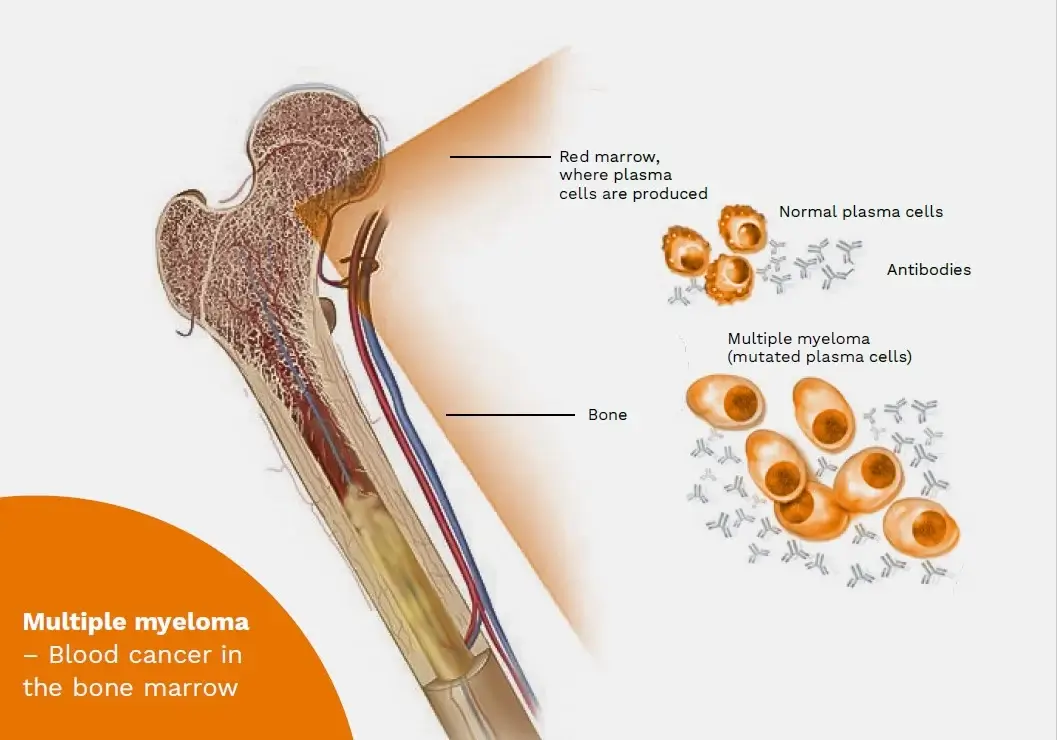
CAR-T therapy has also been investigated as a potential treatment for multiple myeloma, a type of blood cancer that affects plasma cells in the bone marrow. Multiple myeloma is a complex disease, and CAR-T therapy offers a promising approach to target and eliminate malignant plasma cells.
Several clinical trials have been conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of CAR-T therapy in multiple myeloma. These studies have shown encouraging results, particularly in patients who have relapsed or become refractory to standard treatments. CAR-T therapy has demonstrated durable responses and improved overall survival in some cases.
Different CAR-T constructs have been explored, targeting various proteins expressed on the surface of myeloma cells, such as BCMA (B-cell maturation antigen). BCMA-targeted CAR-T therapies, such as idecabtagene vicleucel (ide-cel), have shown promising outcomes in clinical trials and have received regulatory approvals in certain regions.
However, challenges remain in the application of CAR-T therapy for multiple myeloma. The heterogeneity of the disease, antigen escape mechanisms, and potential toxicities are areas that require further understanding and optimization. Additionally, manufacturing CAR-T cells at scale and reducing the treatment cost are important considerations for broader accessibility.
Ongoing research and clinical trials continue to explore novel CAR-T constructs, combination therapies, and strategies to overcome these challenges. CAR-T therapy holds significant potential to revolutionize the treatment landscape for multiple myeloma, offering new therapeutic options for patients who face limited treatment options.

CAR-T (Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell) therapy has emerged as a revolutionary treatment for leukemia, a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. This therapy involves modifying a patient’s own T cells to express CARs, enabling them to target and kill leukemia cells.
CAR-T therapy has shown exceptional success in treating different types of leukemia, including acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Clinical trials have demonstrated high response rates and long-term remissions in patients who have relapsed or become refractory to standard treatments.
For ALL, CAR-T therapies targeting the CD19 protein, such as tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) and axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta), have been approved and shown remarkable efficacy. They have achieved complete remission in a significant proportion of pediatric and adult patients.
In CLL, CAR-T therapy targeting CD19 and CD20 proteins has shown promising results in clinical trials. These therapies have demonstrated high response rates and prolonged remissions in patients with relapsed or refractory CLL.
While CAR-T therapy has shown impressive clinical outcomes, challenges persist. Managing side effects, such as cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxicities, is crucial. Improving the manufacturing process for CAR-T cells to ensure consistency and reducing the associated high costs are also important considerations.
Research continues to improve CAR-T therapy for leukemia, including exploring new targets, developing novel CAR designs, and combining CAR-T therapy with other treatments to enhance efficacy.
CAR-T therapy represents a paradigm shift in leukemia treatment, offering potential cures and prolonged survival for patients who have limited treatment options. Ongoing advancements and efforts to address challenges will further enhance the effectiveness and accessibility of CAR-T therapy for leukemia.
Top hospitals for CAR T-Cell therapy in China

First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University
In the field of CAR T-cell treatment, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, situated in Zhengzhou, China, has become a well-known organisation. The hospital has made tremendous progress in maximising the potential of CAR T-cell therapy for patients by placing a major emphasis on
Top doctor’s for CAR T-Cell therapy in China
Take expert second opinion on CAR T-Cell therapy infusion from best researchers in China.

Peihua (Peggy) Lu, M.D.
“Leukaemia, multiple myeloma, lymphoma, aplastic anaemia, acute and chronic myeloproliferative disorders.
CAR T cell immunotherapy.”

Xian Zhang
“Leukaemia, multiple myeloma, lymphoma, aplastic anaemia, acute and chronc myeloproliferative disorders, myelodysplastic syndrome. CAR-T cell immunotherapy, autologous HSCT.”

Junfang Yang
“Leukaemia, multiple myeloma, lymphoma, aplastic anaemia, acute and chronc myeloproliferative disorders. CAR-T cell immunotherapy.”

John Doe
“Leukaemia, multiple myeloma, lymphoma, aplastic anaemia, thrombocytopeia. Autoimmune blood diseases.”





